
Content:
- Payback period of a heat pump.
- Features of the system, information from experts.
- Payback of a heat pump for home heating.
- How does a heat pump work?
- What is a heat pump?
- How quickly should investments in a heat pump pay off?
- Conclusions.
Undoubtedly, the decision to install a heat pump is quite complex and raises many questions: is it worth investing in this technology, is it profitable, what is the payback period of a heat pump? That's why you should definitely consult a specialist before making such a decision.
The pump has its own operating characteristics; it can serve not only as a source of heat in winter but also provide cooling in summer. Therefore, the installation of a heat pump should be considered in conjunction with other systems in the house. During the heating season, heat is lost from the house through the outer walls, floor and roof, and through the windows. The more efficient and better the insulation of the house is, the better the windows are, the less heat loss through them in winter.
Such a system will require a smaller boiler or heat pump, which will significantly reduce operating costs. In a modern house, it is also important to provide a ventilation system to ensure fresh air and comfortable living conditions. Heating fresh air in winter can consume a significant amount of heat energy (on average, 30% of the heat loss of the entire building), so installing a ventilation system with recovery will also significantly reduce costs. And all these systems can, of course, be effectively combined with a heat pump.
What to consider
If you are already using a system with a gas boiler for heating, then with the current tariffs for natural gas and electricity, installation will not guarantee you immediate significant cost savings. However, a combined system based on a heat pump and a gas boiler will definitely provide you with greater independence and comfort, the ability to choose your heat source depending on the tariffs for natural gas and electricity in the future, because the pump is an investment in your independence for many years.
However, if you are currently using an electric boiler to heat your home, a heat pump will be a reliable option to significantly reduce the electrical power consumed and save money on your electricity bills several times.
It will pay off faster than heating with a pellet boiler or a wood log boiler.
Solid fuel boilers require significant resources and time to clean them during operation, ensure the composition of fuel (logs or pellets), and timely cleaning of the chimney from soot. For a heat pump, the only thing that matters is the availability of the necessary electrical power.
The figure shows the approximate operating costs for heating a 150m2 house in Kyiv with an average level of insulation when using different types of fuel.
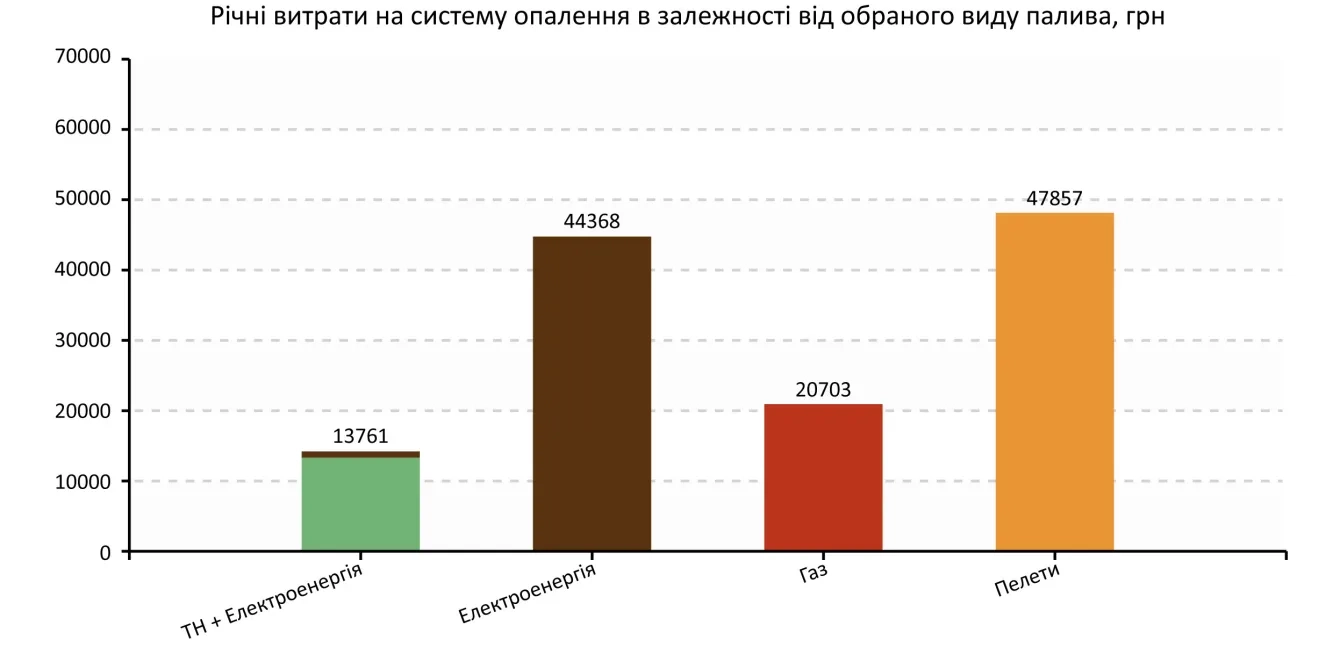
It should also be noted that it is also an environmentally friendly source of heating. During the operation of the heat pump, there is no "chimney", no emissions of harmful substances that destroy the ozone layer of our planet, and the installation will be a responsible decision in relation to our future generations.
When planning to install a heat pump, ask yourself 5 important questions:
Does the house have high-quality thermal insulation to minimize heat loss in winter?
What is the available electrical power for installing the pump?
Is it possible to operate the heating system at a temperature of no more than +55°C?
Is it necessary to install a second (backup) boiler?
Is it possible to use the heat pump not only for heating and hot water heating, but also for cooling?
Features of the system
The payback period and the efficiency of the heat pump depends on the temperature of the heat transfer medium. Depending on the model and type, they can heat the coolant to temperatures of +60...+70°C. However, the efficiency of the heat pump directly depends on the supply temperature: the lower the supply temperature of the heat pump, the higher the efficiency of the heat pump, and the lower the electrical power it consumes.
A high heat transfer medium temperature is required to heat hot water to a comfortable temperature. But the heating system for a heat pump should be low-temperature. And the lower the temperature of the heating medium in the heating system, the more efficiently the heat pump will work.
The table shows an example of the COP value of an air source heat pump at different values of the heat transfer fluid temperature and the outside air temperature.
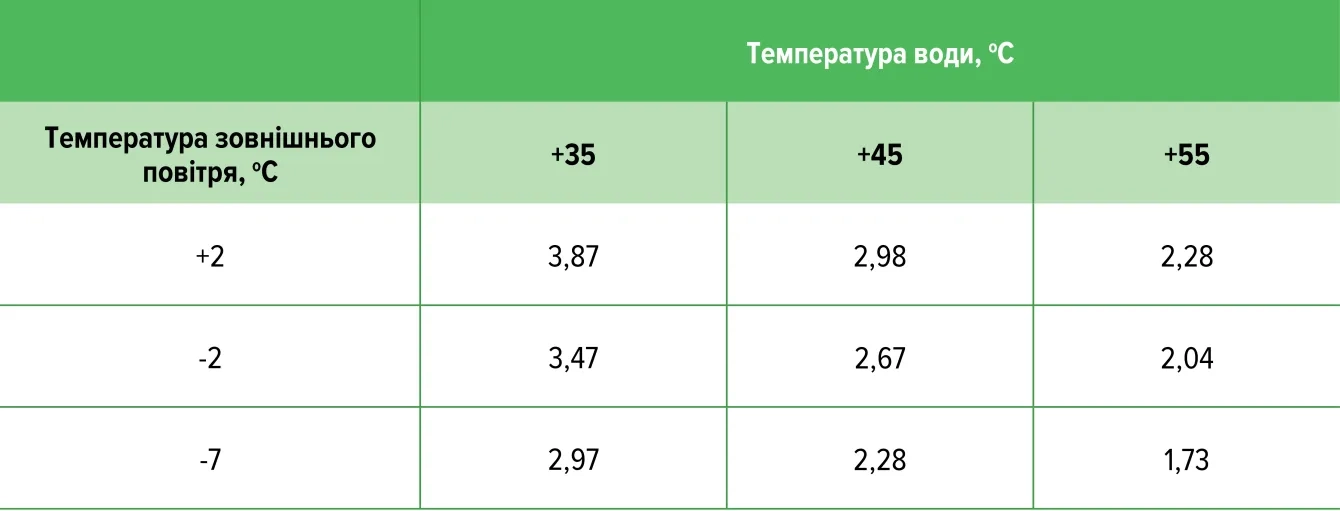
For reliable operation of the heat pump, it is necessary to have a reserve of the required electrical power. If the house does not have the full electrical power reserve, then it is necessary to consider installing an additional backup boiler.
The heat output of the air-to-water pump depends on the outdoor temperature.
The lower the temperature, the less heat output the heat pump will generate. Modern air-to-water heat pumps operate at outdoor temperatures down to -25...-27°C. However, during these periods, their heat output will decrease significantly, and in such cases, you should also consider installing a backup additional boiler.
According to experts, installing a heat pump system has many advantages: it is a reliable and environmentally friendly source of heat, operating costs will be lower than when using any boiler, a heat pump can replace air conditioners in the house and can also be a source of cold in the summer.
But if you decide to invest in a heat pump, you will probably ask yourself whether it will be a good financial investment and what is the actual payback period of a heat pump.
Payback period of a heat pump for home heating
- this is a rather important question, because compared to a standard gas boiler, the price of a heat pump is significantly higher. You can get the calculation of the payback period of a heat pump from the relevant specialists.
It is based on a comparison of the tariffs for the energy carriers available in each case (electricity, natural gas, pellets, etc.), the required capacity for heating and cooling systems, and includes both initial investments and the cost of servicing the equipment during operation.
What do you need to consider?
When calculating the payback period of a system, engineers calculate the amount of heat energy that the building will need during the heating season for a year. The consumption of hot water per day for domestic needs (shower, bath, etc.) is taken into account, and the required cooling capacity for cooling the house in summer is calculated.
Based on these values, the boiler room equipment is selected and the consumption of various energy resources is calculated. For example, the consumption of the required amount of natural gas during the operation of a gas boiler, the consumption of pellets during the operation of a pellet boiler, or the electric power consumed during the operation of a heat pump, the electric power consumed during the operation of air conditioners in the summer to cool the house.
When calculating the payback, the annual maintenance costs of the system and boiler room are also calculated. It is important to note that the air-to-water system does not require any permits, and maintenance is as simple as possible and consists mostly of monitoring the heat pump's operating parameters.
The shortest payback period will be for those systems where the heat pump is used not only for heating but also for cooling. In the case of operating a heating system with predominantly low coolant temperatures. After considering all these factors, you will be able to determine the payback period and financial value of the proposed system.
What is a heat pump?
Aheat pump is an environmentally friendly source of heat, an alternative to traditional gas or electric boilers. During operation, a heat pump consumes electricity, but converts it into heat output with very high efficiency. For example, an electric boiler, consuming 1 kWh of electricity, also delivers 1 kWh of power to the heating system. A heat pump, on the other hand, when consuming 1 kWh of electric power, delivers up to 5 kWh of useful heat output.
During the operation of any boiler, energy from the combustion of different types of fuel is used. For example, a gas boiler uses thermal energy released during the combustion of natural gas.
And during the operation of such a boiler, it is necessary to pay for the amount of gas that is burned in it. Heat pumps, on the other hand, use absolutely free energy from the environment: air, water, soil, etc.
Therefore, the costs of operating a heat pump will always be lower than those of any boiler that burns fuel. However, the initial investment in a heat pump system will be higher, as it is necessary to equip the system to extract ambient heat.
There are different types of heat pumps: "Air-to-water, water-to-water, and ground-to-water, depending on what is the source of energy for the heat pump.
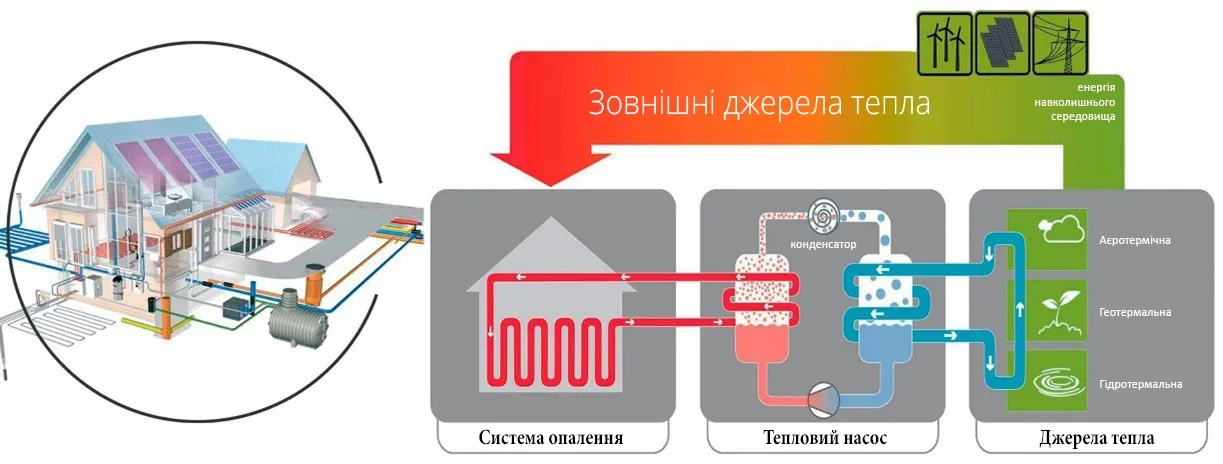
For example, a groundwater heat pump that uses the free heat of the earth. For such a heat pump, a special heat exchanger must be installed outside the house in the ground, where the heat carrier will be heated by the temperature of the surrounding soil. This can be a horizontal or vertical heat exchanger, in which the heat carrier will be heated to a temperature of +3...+8°C, which is quite enough for the heat pump to operate efficiently. For a water-to-water heat pump, two water wells are usually required.
The water is circulated from one well to another using a standard submersible pump, and through a heat exchanger, it transfers the heat of water with a temperature of +8...+10°C to the heat pump. For air-to-water heat pumps, it is necessary to install a heat exchanger in the form of an outdoor unit outside the house, which looks like a familiar outdoor unit of a conventional air conditioner. Modern heat pumps efficiently use the energy of the outside air even at temperatures as low as -25°C.
The heat pump uses the energy from the environment to heat the water in the heating system. A water temperature of +8°C or air temperature of -10°C is sufficient for the heat pump to operate efficiently and heat water in the heating system up to +60°C.
But, as we said earlier, the payback period and efficiency of the heat pump increases at a lower water temperature in the heating system. For example, in a heating system with underfloor heating, the temperature of the heat carrier is approximately +35...+40°C, and the temperature of the heat carrier in a heating system with radiators is on average +55...+60°C. The electrical power consumption of the heat pump in a system with radiators will be at least twice as high as in a system with underfloor heating.
How does a heat pump work?
The heat pump is built on the basis of a refrigeration module - it is a closed, sealed module, its main components are two heat exchangers, a compressor, a thermostatic valve (TRV), and control automation. The refrigerant (freon) circulates in the refrigeration module.
It is circulated by a compressor between two heat exchangers. The main property of the refrigerant is that it can boil and turn into steam at low temperatures. It can even boil at temperatures below 0°C. To describe the operation of a heat pump in general terms, let's use the example of a water-to-water heat pump:
- water from a well with a temperature of +8°C enters the first heat exchanger of the heat pump, where it transfers heat to the refrigerant. At the same time, the water is cooled to a temperature of approximately +5°C and drained back into another well;
- the refrigerant in the heat exchanger boils from this temperature of +8°C and turns into steam (this heat exchanger is called an evaporator);
- the refrigerant in the form of vapor is supplied to the compressor, where it is compressed. During compression, its temperature rises, which can reach up to +100°C. This potential is used to heat the water in the heating system;
- the high temperature refrigerant after the compressor enters the second heat exchanger, where it transfers heat to the heating system water. The refrigerant condenses and turns back into a liquid (this heat exchanger is called a condenser);
- the refrigerant then flows back to the first heat exchanger via a temperature control valve, where it can again take heat from the water.
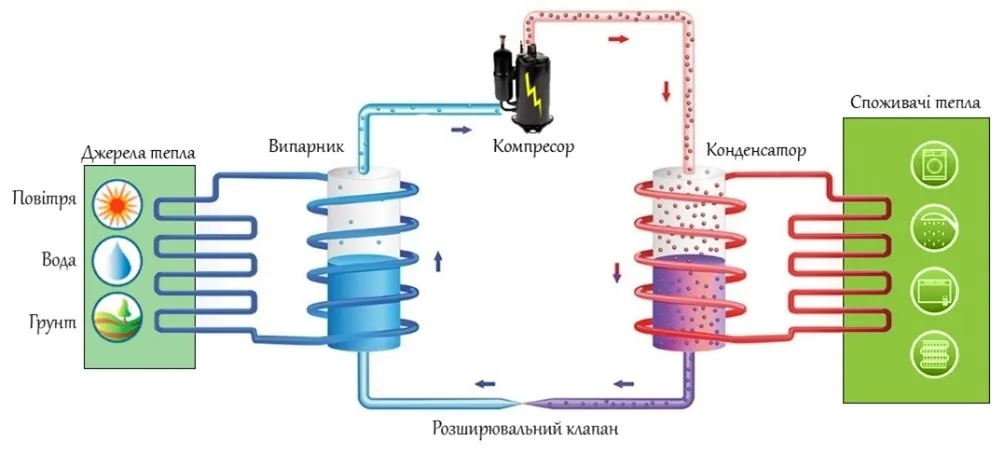
The electricity used by the heat pump is used to run the heat pump compressor. And the higher the temperature to which the refrigerant must be compressed, the higher the electrical power consumption of the heat pump.
If we consider an air-to-water heat pump, the heat of the refrigerant is transferred from the outside air in the first heat exchanger (evaporator). This happens in the outdoor unit of the heat pump, which is installed outdoors. To increase the efficiency of operation, air circulation through the heat exchanger is provided by fans.
How quickly should the investment in a heat pump pay off?
Usually, the payback period for a heat pump system is between 5 and 10 years, depending on the available energy sources (natural gas, electricity, pellets, etc.) and their tariffs.
In new construction, investments in a heat pump can be comparable to investments in natural gas connection (design documentation, pipe laying, purchase of a gas boiler).
It should be borne in mind that the heat pump we are considering has a number of obvious advantages over other traditional heat sources.
Of course, this solution is not absolutely profitable in all respects, which is why many people still hesitate to buy a heat pump. This is mainly due to the high cost of such a system compared to conventional boilers.
The advantages of heat pumps usually include
- minimal operating costs of such systems;
- convenience and safety of use;
- environmental friendliness - no chimney in the house;
- independence from traditional energy sources;
- no need to store and store fuel (wood);
- heating and cooling from one device;
- high reliability in operation.
Conclusions:
The payback period of a heat pump and investments in it can vary. The payback period of 5-10 years may seem quite long, but it will definitely be a reliable investment in your independence, reliability and comfort in operation for many, many years.
That is why such an investment will be truly the most profitable for many in terms of price and efficiency.
Recommended articles:https://mycond.ua/blog/sposoby-zmenshennya-vytrat-na-kvartyrne-budynkove-ofisne-ta-inshi-vydy-opalennya